Human Heart Diagram Introduction
The human heart diagram is one of the most critical educational tools for understanding the circulatory system. It offers a clear representation of the heart’s anatomy, which is essential for students, healthcare professionals, and anyone interested in learning about the human body. A well-drawn diagram simplifies complex processes, such as blood flow, oxygenation, and the working of various heart valves and chambers.
In this guide, we will walk you through the key features of the human heart diagram, explain its importance in education, and explore its applications in both learning and medical fields.
Importance of the Human Heart Diagram in Education
Visual Learning Tool
A human heart diagram is an essential visual learning aid in schools and medical institutions. It helps students, from elementary to university levels, better grasp how the heart works. By labeling each part, such as the left ventricle, right atrium, valves, and blood vessels, students can better understand the heart’s intricate anatomy.
Simplifies Complex Concepts
Understanding how the human heart pumps blood or how blood circulates through different chambers can be difficult without visual aids. Diagrams break down these complex ideas into easy-to-understand components. It’s easier to remember and learn when the heart’s structure and functions are shown in a diagrammatic form rather than just through text.
Boosts Retention
Studies have shown that visual learning aids, such as diagrams, are more effective than text-based learning alone in improving memory retention. When students are asked to recall details about the heart, referring to the diagram can help them remember the structure and its functions more accurately.
Structure of the Human Heart: Key Parts in a Diagram
A human heart diagram illustrates several key components, each of which plays a vital role in ensuring the heart functions effectively. Here are the main parts that should be included in any heart diagram:
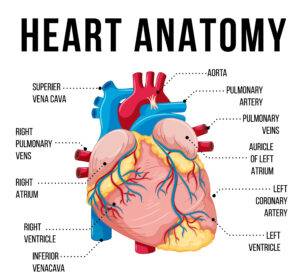
1. Chambers of the Heart
The human heart consists of four chambers:
- Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava.
- Right Ventricle: Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation through the pulmonary artery.
- Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.
- Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body through the aorta.
These chambers work in tandem, ensuring a constant flow of blood to the lungs and the rest of the body.
2. Valves of the Heart
The heart contains four valves that control the flow of blood between the chambers:
- Tricuspid Valve: Between the right atrium and right ventricle.
- Pulmonary Valve: Between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery.
- Mitral Valve: Between the left atrium and left ventricle.
- Aortic Valve: Between the left ventricle and the aorta.
These valves prevent the backflow of blood and ensure that it moves in the correct direction.
3. Blood Vessels
The major blood vessels in the heart diagram include:
- Aorta: The largest artery that carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body.
- Pulmonary Artery: Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
- Pulmonary Veins: Return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
- Superior and Inferior Vena Cava: These large veins carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium.
4. Septum
The septum is the thick wall that divides the right and left sides of the heart. It ensures that oxygenated and deoxygenated blood do not mix.
How Blood Circulates Through the Heart
Understanding the flow of blood through the heart is crucial. Here’s how blood moves through the human heart diagram:
- Deoxygenated Blood enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cava.
- The right atrium contracts and pumps the blood through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
- The right ventricle contracts and sends the blood through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery, which leads to the lungs for oxygenation.
- Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs via the pulmonary veins into the left atrium.
- The left atrium contracts, sending the blood through the mitral valve into the left ventricle.
- Finally, the left ventricle contracts and pumps oxygen-rich blood through the aortic valve into the aorta, which distributes the blood throughout the body.
This continuous circulation is vital for maintaining the body’s oxygen supply and removing carbon dioxide.
How to Draw a Human Heart Diagram
Creating a realistic human heart diagram is a skill that combines knowledge of anatomy with artistic ability. Here’s a basic guide on how to draw one accurately:
1. Draw the Outline
Start by drawing the overall shape of the heart. It should resemble a slightly tilted pear shape, with a broad bottom and a narrower top.
2. Divide the Heart into Four Chambers
Use a vertical line to divide the heart into the left and right sides. Draw the two atria at the top and the two ventricles at the bottom. Make sure the ventricles are larger than the atria, as they are thicker and more muscular.
3. Add the Blood Vessels
- Draw the aorta arching from the top of the left ventricle.
- Add the pulmonary arteries to the right side of the heart.
- Place the superior and inferior vena cava on the top and bottom of the right atrium.
- Sketch the pulmonary veins coming into the left atrium from the sides.
4. Include the Valves
Draw small openings between the chambers to represent the tricuspid, mitral, pulmonary, and aortic valves.
5. Label Everything
Once the drawing is complete, label each part clearly. Use arrows to indicate the direction of blood flow. For clarity, color code the blood flow:
- Red for oxygenated blood.
- Blue for deoxygenated blood.
6. Final Touches
Add shading and details to make the diagram more realistic, and ensure the proportions of the chambers and vessels are accurate.
Educational Uses of the Human Heart Diagram
The human heart diagram is useful in a variety of educational settings:
- School Projects: Students use heart diagrams to explain how blood circulates and how the heart functions in biology assignments.
- Medical Education: Medical students use detailed heart diagrams to study the heart’s anatomy, its chambers, valves, and the pathway of blood.
- Health Education: The diagram is an excellent tool for teaching people of all ages about heart health, how the heart pumps blood, and the importance of maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
Tips for Making a Good Human Heart Diagram
To make an accurate and educational diagram, keep the following tips in mind:
- Accuracy: Ensure that each chamber, vessel, and valve is labeled correctly. Use reliable references such as textbooks or online resources for precision.
- Clarity: The diagram should be easy to read and understand. Avoid overcrowding it with unnecessary details.
- Color Coding: Use red and blue colors to distinguish between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, making the flow easier to follow.
- Legibility: Make sure all labels are clear and large enough to be readable.
- Practice: The more you practice drawing heart diagrams, the more accurate and confident you’ll become.
Conclusion
The human heart diagram is a crucial tool for understanding the heart’s anatomy and the process of blood circulation. By breaking down the complex system into labeled parts, it becomes easier to comprehend the heart’s role in sustaining life. Whether you’re preparing for a biology test, working on a science project, or simply interested in learning more about human anatomy, a well-drawn heart diagram is an invaluable resource.
As you practice drawing and studying heart diagrams, remember to focus on accuracy and clarity. With consistent effort, you’ll deepen your understanding of the heart’s functions and its importance to overall health.