Description
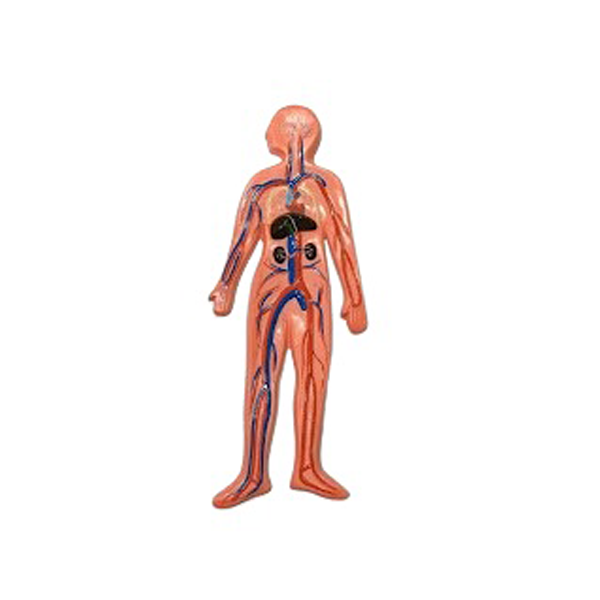
Understanding the Vascular System 2D MODEL
Vascular System 2D MODEL, comprising arteries, veins, and capillaries, is essential for transporting blood, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. To study its complexities, researchers often employ two-dimensional (2D) models, which offer simplified yet insightful representations of vascular structures and functions.
Applications of 2D Vascular Models
- Hemodynamic Analysis: 2D models are instrumental in examining blood flow dynamics within vessels.They help in understanding how blood velocity .
pressure vary across different vessel sections, providing insights into conditions like atherosclerosis - Disease Modeling: By replicating vascular conditions on a 2D plane, researchers can study disease progression, such as tumor-induced angiogenesis or diabetic vasculopathy, under controlled settings.
Advantages of 2D Vascular Models
- Simplicity: 2D models are less complex compared to three-dimensional (3D) counterparts, making them easier to construct and analyze.
- Cost-Effectiveness: They require fewer resources, reducing the cost associated with materials and computational power.
- Accessibility: The straightforward nature of 2D models makes them accessible for educational purposes and preliminary research.
Limitations of 2D Vascular Models
- Lack of Spatial Complexity: Real vascular systems are three-dimensional, and 2D models may oversimplify spatial interactions.
- Limited Physiological Accuracy: Certain physiological phenomena.
such as the curvature of blood vessels and complex flow patterns, are challenging to replicate in 2D models.
Recent Advances in 2D Vascular Modeling
Advancements in computational techniques have enhanced the accuracy and applicability of 2D vascular models. For instance, the development of automated software like VESGEN 2D allows for detailed quantification of vascular parameters, aiding in the analysis of vascular growth and remodeling.
Conclusion
While 2D vascular models offer valuable insights into the vascular system’s function and pathology, they are often complemented by 3D models and in vivo studies to provide a more comprehensive understanding. Nonetheless, their role in simplifying complex vascular phenomena makes them indispensable tools in biomedical research.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.